Servo motor - things to know!
NCS Blog - Servo motors are used in most ring systems where high precision control is required in civil and industrial applications.
Post date: 06-04-2020
3,009 view(s)
Servo motor - things to know!
Posted on 04/04/2020 By TU NGUYEN
How did you know about the terrain robots used in the military for the purpose of detecting bombs and mines to control movement? Or how metal cutting and shaping machines in mechanical processing with the ability to move correctly (milling, turning, stamping)? and how can the antennas accurately control position according to angle and height?
Servo motors are used in most ring systems where high precision control is required in civil and industrial applications.
The servo motor is quite similar to the stepper motor but adds a part to control the accuracy during the moving operation. Learn more about stepping motors through the article: Must understand the stepper motor (Step motor).
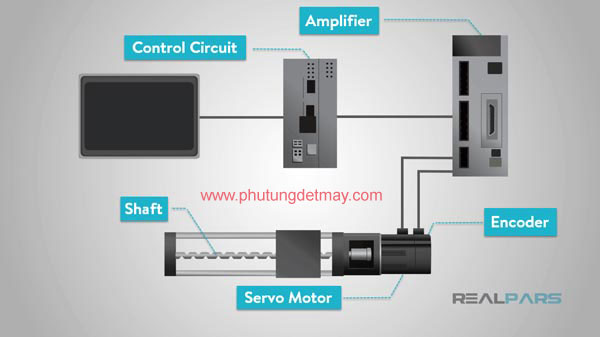
1 / What is servo motor ?
Servo motor is a part of closed-loop system and it includes many components such as control circuit, serrvo motor, shaft, potentiometer, gear disc, amplifier, or encoder or decoder.
Servo motor is an independent electrical device, this is a device to create torque with high efficiency and high accuracy. The motor shaft's output shaft moves at a specific angle, position, and velocity that other conventional motors do not.
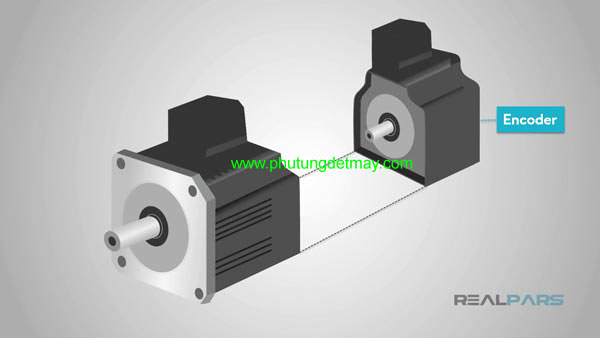
The servo motor is a closed-loop structure with the ability to feedback position signals to control the rotation angle, speed and position. It is easy to imagine this is a normal motor and using the sensor to feedback the position signal to the controller.
The motor is controlled by electrical signals, either analogue or digital. The encoder as a sensor provides feedback signals about speed and position on the controller. This is an electrical mach located inside the motor usually equipped with gear systems (rotating disks).
2 / Servo motor classification
The serco motor is divided into different groups based on its application: AC servo and DC servo.
There are three things to evaluate servo motors: The first is the current (AC, DC), the second is the type of switching used (whether the motor uses a brush or not) and the third is the magnetic field consideration. Rotation of motor, rotor, synchronous or asynchronous.
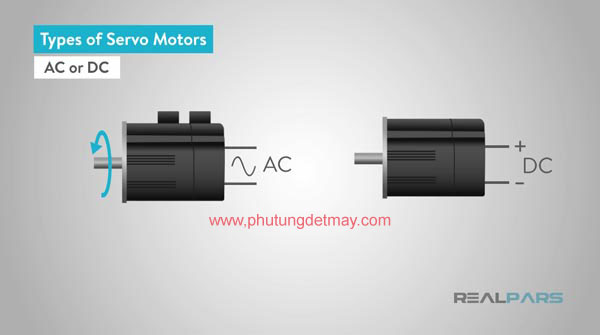
2.1 / AC - DC current
AC or DC is the most basic classification of the motor to be used, from the angle of multiple performance, the difference between AC or DC motor is the ability to control the rotation speed
Speed DC motor is directly proportional to the voltage under constant load condition
Speed AC motors are determined based on the frequency of the voltage and the polarity
When both types of AC and DC servomotors are used in a servo system, the AC motor will be subjected to higher currents and normally used in robots, production lines and other industrial applications (where needing repetition and high precision).
AC or DC servo motor can be either brushless or brushless. The blown type is cheaper and simpler to use, while the brushless type has a more user-friendly design, higher performance and lower noise.
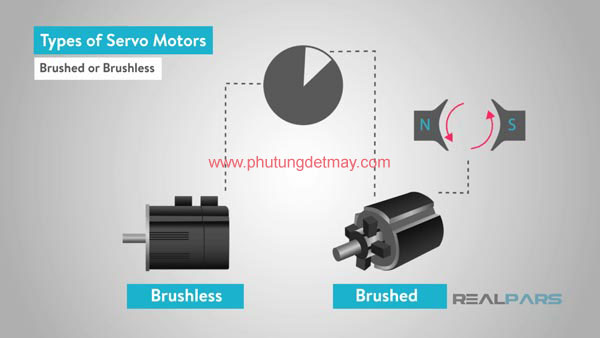
2.2 / Switching type (whether or not to use brushes)
The switch is a rotating electrical switch that reverses the current between the rotor and the trigger circuit. It consists of a cylinder with multiple metal contact segments on the rotor. Two or more electrical contacts are called "brushes", made of a soft conductive material such as carbon, when rotating it creates slip contact with the commutator.
While most of the motors used in AC servo motors are brushless, the permanent magnet brush motor is sometimes used for the purpose of reducing costs and simplifying.
A brushless DC motor replaces the brush and commutator for the purpose of perfecting the switching through the use of a Hall or Encoder sensor.
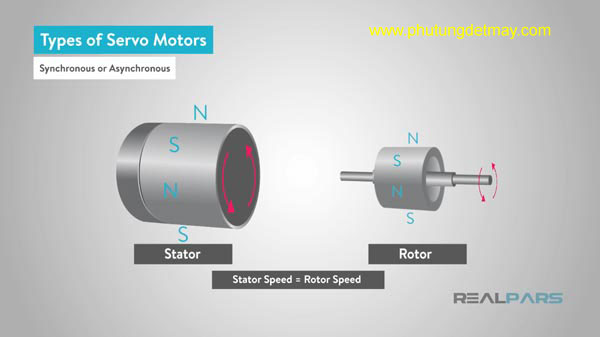
2.3 / Synchronous or asynchronous
While DC motors are classified by brush or brushless group, AC is distinguished by either synchronous or asynchronous.
If you look back on the AC-DC classification, the AC motor has a speed that is determined by the frequency of the voltage and the number of pole pairs. This speed is the sync speed. Therefore, the synchronous motor has a rotor rotation speed similar to that of a magnetic field.
Asynchronous motors are often referred to as induction motors, rotor rotational speeds are slower than magnetic field rotations. However, it is still possible to control the speed of rotation by generally changing the number of poles and changing the frequency
3 / Principle of operation of the Servo motor
3.1 / DC servo
The working principle of DC servo motor is based on 4 main parts, DC motor, position sensor device, gear assembly and control circuit. DC motor speed is based on the applied voltage.
In some circuits, the control pulse is used to generate a DC reference voltage that corresponds to the desired position or speed of the motor.
For digital control, a PLC or motion controller is used to generate periodic pulses that help to create a more precise control.
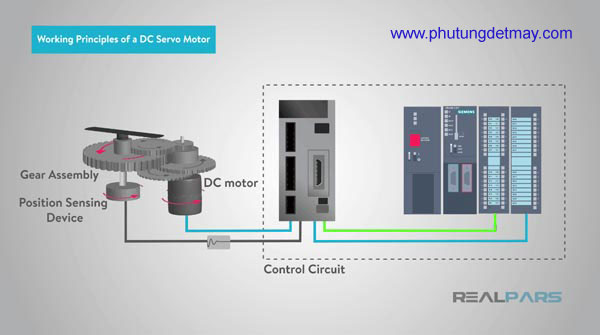
The feedback signal sensor is usually a potentiometer that generates a voltage that corresponds to the absolute rotation of the motor shaft through a gear mechanism. The feedback voltage value is then applied to the amplifier of the difference comparator amplifier.
The amplifier compares the voltage generated from the current position of the motor received from the potentiometer feedback and to the position of the motor generated due to positive or negative voltage differences.
This differential voltage is applied to the armature of the motor. When the difference increases, there will be output voltage applied to the armature of the motor. As long as there is a difference, the amplifier compares the amplified voltage equal to the armature.
The motor rotates until the difference value becomes zero. If the difference is negative, the armature voltage will reverse and so the armature rotates in the opposite direction.
3.2 / AC servo
The working principles of AC servo motor are based on the structure of two separate types of AC servo motor: Synchronous and asynchronous. Synchronous AC servo motor consists of stator and rotor. The stator consists of a cylindrical frame and a stator core.
The induction coils around the stator core and the coil are connected to a conductor that provides current to the motor.

The rotor consists of a permanent magnet and this is different from the asynchronous induction rotor in that the current in the rotor is generated by electromagnetism and is therefore called brushless servo motor.
When the stator magnetic field is excited with voltage, the rotor follows the stator's rotating magnetic field at the same speed or is synchronized with the stator's excitation field and this is where the synchronous type comes from.
With this permanent magnet rotor, no current is required in the rotor so when the stator field stops, the rotor stops. These motors are more efficient because there is no current in the rotor.
When it is necessary to know the position of the rotor against the stator, the encoder is placed on the rotor and provides feedback feedback to the servo motor controller.
4 / Application of Servo motor
Servo motor applications are applied in many industrial and commercial systems as with robots, in which the servo motor is used at each joint of a robot to realize its precise movement angle.
The camera's autofocus uses the built-in servo motor to precisely adjust the position of the lens to sharpen out-of-focus images.
Antenna positioning systems in which the servo motor is used for both azimuth and azimuth positioning of antennas and telescopes, such as those used by the Infinite Astronomical Observatory national route.
Source : From Internet.










Send your comment